Tag: Audit
For most organizations, audits are treated like a finish line. You prep, survive the chaos, hand over your evidence, and then you move on.
But in the rush to wrap things up, many teams miss the final and arguably most important phase: learning from your most recent audit cycle and making improvements for the next one.
That’s the value of the audit feedback loop: a structured process for gathering auditor feedback that can be analyzed and acted on.
Feedback loops transform audits from reactive checklists into strategic growth tools that benefit your organization’s security and compliance efforts. When implemented effectively, these loops can make your next audit smoother while creating lasting operational efficiencies that benefit your entire organization.
Modern audit management platforms like Thoropass help organizations set up the audit workflows needed to enable these feedback opportunities. Read on to learn more about the value of feedback loops and how they address the disconnects dragging down your audit process.
Feedback loops: The solution your audit process needs
At Thoropass, an audit feedback loop is our term to describe the communication cycles that happen during and after an audit. These loops capture key learnings—both from successful interactions and pain points—that can then guide future improvements to your auditing and compliance processes.
“We actually track the number of loops in every engagement.” Joe Hunsicker, Sales Solutions Engineer at Thoropass, explains. “Some of those are necessary—clarifications, additional context, etc.—but others are inefficient. They happen because something wasn’t scoped clearly or the right context wasn’t communicated.”
The ultimate goal, according to Hunsicker, is to “reduce the number of unnecessary loops—while encouraging the valuable ones that make your program stronger.”
To illustrate the difference, here’s how traditional audits compare to feedback loop-enhanced processes:
Traditional Audit Workflow:
- Auditor requests evidence
- Organization provides documentation
- Auditor identifies gaps or issues
- Organization scrambles to address findings
- Audit concludes with report delivery
- Organization files away the report until next year
Feedback Loop-Enhanced Workflow:
- Auditor requests evidence with clear context
- Organization provides documentation through centralized platform
- Real-time clarification and quality discussions occur
- Issues are addressed collaboratively with an understanding of the business context
- Audit concludes with strategic recommendations
- Post-audit analysis identifies process improvements for future cycles
These loops occur at multiple stages: during evidence collection when clarification is needed, during testing when controls require deeper explanation, and—crucially—after audit completion when strategic insights can be captured and applied. The most overlooked feedback is often uncovered in this final phase, informing strategic recommendations for process improvements that go beyond compliance requirements to guide operational efficiencies and security enhancements.
Without feedback loops, organizations often find themselves caught in cycles of miscommunication, last-minute scrambling, unnecessary rework, and repeated mistakes across audit cycles. But with structured feedback mechanisms in place, audits become collaborative partnerships where both parties—auditors and the organizations they collaborate with—work toward the shared goal of improving the organization’s security posture.
The value of a feedback loop in the audit process
When organizations implement structured feedback loops in their audit processes, they create a cycle of continuous improvement that delivers tangible value across four key areas: time optimization, operational clarity, communication, and process improvement.
1. Reallocating time back to the business
By eliminating redundant communications and streamlining evidence collection through clearer upfront context, feedback loops reduce the back-and-forth that typically consumes audit cycles.
“Organizations have more time to focus on the things that are pressing to their business,” Hunsicker notes. “They can get their reports faster, spending less time on compliance and audit, and more time on security and whatever business they’re building.”
By reducing time spent navigating audit confusion, compliance teams can shift focus from reactive firefighting to proactive security improvements.
2. Better internal organization and clarity
“Feedback loops can create less internal strife because they establish a structured process for communicating effectively between the auditor and across teams,” Hunsicker explains.
Instead of scrambling to understand requirements and locate evidence, teams operate with consistent processes and clear communication channels. The result is reduced stress, better preparation, and more meaningful engagement with the audit process.
3. Better communication with your auditor
Modern audit platforms facilitate feedback loops by creating repeatable workflow processes that improve communication between the auditor and the business.
Better communication makes it easier for auditors and their businesses to build a more productive partnership over time. Feedback loops turn two-way communication into a fixture of the auditing process, using a finite number of communication touchpoints to ensure ongoing feedback through a structured system that doesn’t risk overwhelming or confusing your auditor.
4. An audit trail of feedback for future analysis and improvement
By building feedback loops into your auditing workflows, your organization benefits from embedded, repeatable processes that are designed to support ongoing analysis and improvement.
This transparency eliminates the email chains, assorted spreadsheets, and document version confusion that plague traditional audits. More importantly, it creates an audit trail of feedback that can be analyzed and improved upon for future cycles.
Feedback loops also change how teams relate to their auditors. Instead of being subject to a one-sided evaluation, audits become more of a collaborative partnership.
“Feedback is good,” Hunsicker says. “It’s what people want from an audit relationship. They want someone knowledgeable who can challenge their assumptions and act like an advisor instead of someone just checking boxes.”
The components of an impactful feedback loop
A strong audit feedback loop doesn’t happen by accident. It’s built from clear roles, intentional communication, and a shared commitment to improvement.
Here are the components every audit feedback loop needs to feature:
1. Value-added questioning
The most impactful feedback goes beyond basic compliance checking to explore the why behind controls and processes: “A value-add comment like, ‘Can you clarify what you meant by X?’ shows that folks are looking to improve,” Hunsicker explains. “It’s all about giving feedback on things that don’t appear quite right to help propel the audit process and business forward.”
This approach transforms audits from checkbox exercises into strategic consultations. When auditors ask, “This control operates flawlessly, but why are you doing this?” they’re creating opportunities for organizations to evaluate whether security investments align with actual business needs and risk profiles.
The key is framing questions through a helpful lens rather than a punitive one. “Those value-added loops occur when a third party independently evaluates a system and produces a conversation that otherwise might not have taken place,” notes Hunsicker. These conversations often reveal opportunities for simplification, automation, or strategic realignment that internal teams might miss.
2. Strategic partnership approach
Successful feedback loops require both parties to view the relationship as a partnership rather than an adversarial evaluation. “Feedback loops go beyond just checking the box: Did you do this or that?” Hunsicker says. “That yes/no appraisal is not the focus of an audit process.”
This partnership mentality encourages open communication about challenges, constraints, and objectives. When organizations feel comfortable discussing why certain controls exist (“it’s a contractual requirement”) or what business pressures they face, auditors can provide more relevant and actionable feedback.
3. Defined roles and responsibilities
Clear role definition ensures feedback loops remain productive rather than overwhelming. “It’s about clarifying the relationship and roles between the auditor and auditee,” Hunsicker explains. “There’s a team of auditors, generally a lead auditor—in our case, we call it an audit delivery manager—that would be responsible for feedback.”
Organizations should designate specific team members to participate in feedback discussions, ensuring consistency and preventing communication overload. These designated contacts serve as translation layers between technical audit requirements and business operations, facilitating more meaningful exchanges.
4. Focus on quality over quantity
Not all feedback is valuable feedback. The most effective feedback loops limit the number of touchpoints to prioritize quality communication over high-volume feedback that can muddle messaging and overwhelm recipients.
“We want to paint the picture that we’re here to understand so that we can have more meaningful interactions and more meaningful feedback loops—as opposed to the unnecessary ones that kind of plague our industry,” Hunsicker notes.
This quality focus requires both auditors and organizations to prepare thoroughly, communicate clearly, and engage substantively. The goal is reducing total communication volume while increasing the strategic value of each interaction.
Close the gap between audit and process improvement
By capturing the right insights and embedding them into your processes, feedback loops turn each audit into an opportunity to strengthen your team’s knowledge, systems, and collaboration. You can reduce repeat mistakes, surface strategic conversations, and prepare for future audit frameworks with confidence, not dread.
Thoropass enables this shift. With tools to facilitate real-time communication, identify framework overlap, and track meaningful touchpoints across audits, our platform turns feedback from an afterthought into an engine for value-added auditing and continuous compliance.
Ready to modernize your audit process? Schedule a discovery session with Thoropass.
Cloud adoption is accelerating. Security automation is evolving.
But the way we handle audits? It’s still stuck in the past.
Compliance teams today are managing audits with the same reactive, manual playbooks they’ve used for years—despite new tools that promise better outcomes. It’s no wonder audit season still feels like a fire drill complete with last-minute scrambles, endless email chains, and that familiar sense of dread when the auditor’s first request hits your inbox.
But there’s a better way—one that transforms audits from chaotic ordeals into streamlined, collaborative processes.
In this article, we’ll explore why the traditional audit model is broken, what the “new way” looks like, and how forward-thinking compliance leaders are already reaping the benefits of a more integrated approach.
The current landscape of the audit model and why it’s broken
Audits haven’t changed much in decades. They’re still largely treated as one-off events—a point-in-time snapshot where a clean report is the only goal.
The reality is more complex. Today’s frameworks (SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc.) demand continuous control, stakeholder involvement across teams, and credible evidence that your security program is working.
And yet most organizations still rely on outdated tools and fragmented processes. That gap between what audits require and how they’re executed creates major friction for the both auditor and auditee.
Many companies view audits as solely an IT function
Instead of treating audits as a business-wide initiative, many companies silo the responsibility within IT. That leads to bloated scopes, missed risks, and controls that don’t reflect the actual business context. Add multiple departments, four or more auditors, and disconnected evidence requests, and you’ve got a recipe for disaster.
The thing is, these frameworks are not IT specific. Security isn’t just relegated to the IT function. It’s an organizational and people problem just as much as it is a technology problem.
This misunderstanding leads to poorly scoped audits that miss the business context entirely. Poorly scoped audits can lead to a false sense of security, or potentially worse – wasted time focusing on risks that are not pressing to the business or the users of the audit reports themselves.
The audit gap across industries persists
If you’ve ever sat through a chaotic audit cycle and thought, “This shouldn’t be this hard,” you’re right. There’s a reason the audit season comes with a lot of stress every year. And it’s not because your team isn’t capable or committed.
It’s because of what we call the audit gap: The disconnect between a company’s audit preparation and auditors actual expectations.
Here’s what that looks like in practice: Your compliance team spends months gathering logs, maintaining controls, and documenting policies. But when the audit begins, the auditor shows up with a long list of evidence requests—and suddenly none of your prep feels like it “counts.”
Documents get sent over email. Requests are unclear. Version control gets messy. And you’re fielding repetitive questions from someone who may not even understand your environment.
And that’s not just frustrating—it’s costly. All of this back and forth can delay certifications or tank deals with prospects who want fast, confident proof of your security posture. .
Worse, your best people are pulled away from high-impact work to chase down evidence or re-explain decisions to an auditor who’s out of sync. You start to burn out. Not just because audits are hard—but because the whole process is disconnected.
The tools problem adds more work
While technology has advanced dramatically in other areas of security and compliance, the audit process itself remains largely manual. Spreadsheets, email chains, and ad-hoc file sharing still dominate the evidence-collection process.
Even organizations with sophisticated governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) platforms often find themselves reverting to manual processes when audit time arrives—usually because their auditor requires it and because their systems don’t talk to each other.
The ripple effects of this broken model extend far beyond productivity loss. Teams burn out from the constant firefighting and your security program actually gets worse.
The solution to a better audit season
Instead of treating compliance preparation and audit execution as separate processes, forward-thinking organizations should focus on integrating them into a unified workflow, bridging the audit gap that exists between traditional audits and your compliance workflows.
Here’s what that looks like with Thoropass:
1. Preparing for audit success from day one
Rather than guessing what auditors might want, our platform and expert services provide compliance teams with proven control recommendations based on common industry-agnostic security risks as a security program baseline. Once the baseline is set, teams are freed up to consider unique risks and develop controls to further protect their organization.
Thoropass offers a list of controls that, in our experience, have been broadly accepted in the market. So from the start of your audit process, you not only see what we recommend but have the confidence to deploy resources that will hit your audit targets.
This approach eliminates the guesswork that plagues traditional audit prep, giving teams confidence that their efforts will align with auditor expectations.
2. Project management that gets you compliant faster
After the control parameters are established, the next challenge is operationalizing those controls.
Thoropass can help you project manage and prioritize recommendations to get compliant with whichever framework you need. This function ensures that compliance activities stay on track and that nothing falls through the cracks—a common problem when audit prep is managed through spreadsheets and email.
3. Automated evidence collection
Manual evidence gathering is one of the biggest time sinks in traditional audits. No more digging through email chains or SharePoint folders. Thoropass integrates directly with over 100 source systems to pull relevant evidence automatically.
This not only saves time—it improves accuracy, ensures traceability, and makes it easier to maintain a state of readiness between audits.
4. Built-in auditor collaboration
Here’s where things get really interesting: While many vendors focus on either client-side compliance tools or auditor-facing platforms, Thoropass provides integrated technology for both sides of the audit relationship, which fit together hand and glove.
That means shared visibility, fewer misunderstandings, and less back-and-forth during audit season. By enabling real-time collaboration between compliance teams and auditors, we eliminate many of the communication breakdowns that cause delays and frustration.
The benefits of the new audit model
When compliance and audit processes are properly integrated, the benefits extend far beyond just easier audit seasons. Organizations see improvements across multiple dimensions of their security and compliance programs, including:
Full GRC adoption
Integrated platforms naturally encourage broader adoption of governance, risk, and compliance practices across the organization. When audits become less painful, stakeholders are more willing to engage with compliance requirements year-round rather than treating them as annual fire drills.
Enhanced security posture and compliance
By maintaining continuous visibility into control effectiveness, organizations don’t just achieve compliance—they actually improve their security posture. The ongoing monitoring and evidence collection provide real-time insights into potential vulnerabilities and control gaps.
Consolidated framework management
Many organizations need audit reports or certifications for SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI DSS, and other frameworks. Traditional approaches require separate audit processes for each framework, leading to significant duplication of efforts.
With an integrated approach, organizations can leverage the average 70% overlap that typically exists across frameworks. For example, to do an ISO certification and SOC 2 at the same time, Thoropass aligns both timelines and issues one single request list. That way, there’s no duplicate efforts requesting the same information for multiple audits.
Faster time to certification
When auditors and compliance teams work from the same platform with the same data, audit cycles naturally accelerate. Clients using Thoropass have cut their time to audit by more than half.
Improved communication and collaboration
Integrated platforms transform the relationship between organizations and their auditors. Instead of potentially adversarial interactions caused by constant clarification requests, teams can collaborate more effectively toward shared objectives.
With one connected system, everyone knows where the audit stands—what’s been submitted, what’s approved, and what needs fixing. Auditors give feedback in real-time instead of after weeks of silent testing.
Real-world results
The benefits of this new audit model aren’t just theoretical. Matt Steel, Head of GRC at The Access Group, says the transformation “has made massive differences in terms of our costs and our resource requirements, and has saved us a vast amount of time. Generally, a SOC audit could’ve taken us 12 months from beginning to end, and now we’re probably doing it in six or seven months.”
The Access Group also eliminated the communication challenges that plagued their previous audit processes: “We’ve had a lot of challenges with the audit process that we inherited. Communication was really difficult,” Steel says. “We had four different auditors, and each of them wanted the evidence in their own specific way. All of it was done through email chains and we had version control issues.”
With Thoropass, The Access Group cut audit timelines by 50%, reduced external consulting costs by 25%, and reclaimed hours of internal time. More importantly, they now approach compliance as a continuous, strategic effort—not a one-off scramble.
Integrated auditing is the future
By closing the audit gap and embracing integrated compliance and audit platforms, your organization can eliminate the chaos, reduce costs, and build a security program that actually supports growth. It’s time to stop surviving audit season—and start owning it.
Ready to transform your audit experience? Schedule a discovery session to see how Thoropass can help you close the audit gap and modernize your compliance program.
Compliance with ISO 27001 standards can be an uphill battle for large enterprises. Endless audit cycles, manual processes, and unpredictable costs make the experience grueling, especially for compliance teams tasked with ensuring information security. If you’re responsible for audits, chances are you’ve felt stuck in an “audit pain” cycle that seems impossible to escape. But it doesn’t have to be this way.
In this blog post, we’ll tease apart the ISO 27001 audit process, address common pain points, and show you how Thoropass simplifies compliance for enterprise success.
Key takeaways
- ISO 27001 audits are essential for achieving and maintaining certification but are often fraught with inefficiencies
- Understanding the stages of the audit process and common challenges can help enterprises prepare more effectively
- Thoropass offers a streamlined, purpose-built platform to simplify audits, reduce costs, and save time
Stages of an ISO 27001 audit: Why audits feel like an endless loop
For a compliance leader at a growing enterprise, the ISO 27001 audit cycle can feel like a never-ending treadmill. Just as you complete one phase, another begins–draining resources, monopolizing team bandwidth, and pulling focus from strategic initiatives that could drive your business forward.
Let’s break down why this cycle feels so relentless: As your information security management system evolves with your growing business, each phase of the audit process requires extensive preparation, coordination across departments, and meticulous documentation. For large organizations, this means hundreds of hours spent gathering evidence, managing stakeholder communications, and responding to findings – only to start the process again.
What makes this particularly challenging for large enterprises is the compounding effect: While smaller companies might manage a linear audit process, enterprises must often juggle multiple frameworks, geographical requirements, and overlapping timelines simultaneously. This means your team could be preparing for a surveillance audit in one region while conducting a risk assessment in another–all while trying to maintain daily security operations and drive business growth.
1. Internal audit and audit report
Before external validation begins, you’ll need an independent internal assessment. While any team not involved in implementation can perform this audit, many enterprises find this initial stage challenging due to resource constraints and coordination complexity. Thoropass compliance architects can guide your team through internal audit preparation and documentation, reducing the burden while preserving auditor independence.
2. Stage 1 of the initial certification audit
The first formal stage examines your ISMS design. While traditionally conducted in person, many enterprises now opt for remote audits to accommodate global teams and complex organizational structures. Your auditor will evaluate the following:
- Policies and procedures documented in your ISMS
- Critical and non-critical findings that could impact Stage 2
- Your Statement of Applicability and overall security design
Note: Auditors do not necessarily examine Annex A controls. Using your Statement of Applicability, they determine whether the correct level of information security has been designed with the ISMS.
3. Stage 2 of the initial certification audit
This critical phase examines your ISMS in action—a particularly challenging stage for enterprises with multiple departments and locations. Your team must demonstrate:
- Real-world implementation of policies and procedures
- Evidence of controls across all relevant departments
- Practical application of your security framework
- How your ISMS handles complex scenarios, such as employee disciplinary actions
Enterprise impact: Plan for your control owners and key stakeholders to dedicate a full week to audit meetings—a significant investment of senior time and resources.
4. ISO 27001 certification
Finally, you achieve certification: After the Stage 2 audit, your auditor will hold a closing meeting and share preliminary findings. While they can share an initial impression, the final certification decision rests with the certification body. Management should respond in the form of a corrective action plan, which includes:
- The root cause of the issue
- The actions to remediate, and
- A timeline for completion.
Once those action plans have been drafted, the auditor will include them in the audit report, typically completed within 1-2 days of the closing meeting. At this point, auditors should be able to indicate if they believe you will be ISO 27001 certified, but the final decision lies with the certification body.
5. Periodic surveillance audits
As you know, ISO 27001 certification is not a one-and-done event.
While ISO 27001 does not require an annual certification, you must still perform a surveillance audit in the off-years. Two years after your certification, an auditor from a certification body will perform a surveillance audit to ensure that the organization still operates the ISMS and controls as designed.
Surveillance audits include all clauses in the ISO 27001 framework, but only 50% of Annex A requirements are examined each year. (The auditor decides how this is divided.) Additionally, the auditor will revisit any nonconformities found during the initial certification audit and determine whether the organization remediated the issues properly.
At the end of these audits, the auditor will again share any findings with management, similar to the first year, and produce an audit report to the certification body indicating whether the organization still meets the standard’s requirements to maintain certification.
6. Every three years: ISO 27001 recertification audits
You’ll need to repeat the whole certification process in the third year after certification (and every three years thereafter). During this time, your business has likely grown and changed, which means your ISMS and SoA should have changed with it, as reflected in your annual surveillance audits.

How to eliminate friction between compliance and audit for time and cost savings
Common pain points of ISO 27001 audits for enterprise companies
For enterprise organizations, ISO 27001 audits present unique challenges that grow exponentially with company size. What might be manageable pain points for smaller companies become major operational hurdles when scaled across thousands of employees, multiple departments, and various geographical locations.
Manual evidence collection
The sheer volume of documentation required for an enterprise ISO 27001 audit can be overwhelming. Your team spends countless hours hunting down evidence from various departments, following up on missing documents, and ensuring everything is properly formatted and organized. This manual approach not only wastes valuable time but also increases the risk of overlooking critical evidence or submitting outdated documentation, potentially leading to audit findings that could have been avoided.
Siloed teams
In large enterprises, the lack of transparency between departments creates significant barriers to efficient audit process management. When your security, IT, HR, and compliance teams operate in isolation, it becomes nearly impossible to maintain consistent security controls and documentation standards. This disconnection often results in duplicate efforts, inconsistent responses to auditor requests, and a fragmented view of your organization’s security posture.
Resource allocation
Managing an information security management system at an enterprise scale requires a careful balance of resources. Your compliance team is constantly stretched thin, trying to maintain daily security operations while preparing for upcoming audits. This challenge is amplified when dealing with multiple frameworks and certifications, as each requires dedicated attention and expertise. The result? Critical security initiatives often take a backseat to audit preparation, creating potential vulnerabilities in your security program.
Unpredictable costs and timelines
Enterprise certification audits rarely go according to plan. What starts as a straightforward timeline often extends due to unexpected findings, delayed responses from various departments, or the need for additional evidence collection. These delays cascade into increased costs—not just in direct audit expenses but also in the hidden costs of devoted internal resources and delayed strategic initiatives.
Endless audit cycles
Perhaps the most frustrating aspect for enterprise compliance leaders is the perpetual nature of the audit cycle. As soon as you complete your certification audit, you’re already preparing for surveillance audits. Layer in other compliance frameworks, and your team finds themselves trapped in an endless loop of preparation, evidence collection, and response to findings. This constant cycle prevents your team from focusing on strategic security improvements and innovation that could actually strengthen your security posture.
Five ways Thoropass simplifies ISO 27001 audits
Traditional approaches to ISO 27001 audits weren’t designed for the complexity and scale of modern enterprises. Thoropass offers a platform and expert support that streamlines compliance prep, while working in alignment with independent certifying processes.
1. Streamlined process
Eliminate the endless back-and-forth with auditors and time wasted hunting down evidence across departments: Thoropass’s automated workflows transform how enterprises manage their audit process. Our platform provides real-time monitoring and alerts, ensuring you catch potential issues before they become audit findings. When your external auditor requests evidence, everything is readily accessible in one centralized location.
The platform’s collaborative environment breaks down silos between departments, enabling seamless communication between your team and auditors. By centralizing all audit-related activities, documentation, and communications, Thoropass eliminates the confusion and delays that typically plague enterprise ISO 27001 certification efforts. Teams can work simultaneously on different aspects of compliance while maintaining visibility across all activities.
2. Multi-framework capability
In today’s complex regulatory environment, enterprises rarely need to comply with just one framework. Thoropass’s multi-framework approach transforms how you handle evidence collection and management. Upload evidence once, and our platform automatically maps it to relevant controls across multiple frameworks, including SOC 2, ISO 27001, and others. This innovative approach means you can simultaneously satisfy requirements for multiple certifications, dramatically reducing your team’s resource burden.
Through intelligent control mapping and evidence reusability, you can achieve multiple certifications with a single audit effort. This not only saves time and resources, but also ensures consistency across your compliance programs. The platform’s smart tagging and categorization features make it easy to track which evidence satisfies which requirements across frameworks.
3. Purpose-built platform
Thoropass isn’t a generic compliance tool retrofitted for ISO 27001—it’s built specifically to handle the complexities of enterprise ISMS requirements. Our customizable templates guide you through each requirement, while our integration capabilities pull necessary data directly from your existing tools. This purpose-built approach means you’re not wasting time adapting generic solutions to fit your needs.
The platform features intelligent workflows that adapt to your organization’s specific requirements and risk profile. Advanced AI capabilities, including GenAI Due Diligence Questionnaires, help automate routine tasks while ensuring accuracy. Real-time dashboards provide instant visibility into your compliance status, making it easy to track progress and identify potential issues before they impact your audit.
4. Experienced experts at your side
Technology alone isn’t enough. That’s why Thoropass pairs our advanced platform with seasoned compliance experts who understand enterprise-scale challenges. Our team supports you throughout your entire journey, from initial gap analysis through the certification process and beyond. These experts help optimize your compliance program, provide strategic guidance, and ensure you make the most of the platform’s capabilities.
Having access to experienced professionals means you’re never alone in navigating complex audit requirements. Our experts help interpret findings, develop remediation strategies, and provide best practices based on extensive experience with enterprise implementations. This combination of technology and expertise ensures you’re not just checking boxes but building a robust and sustainable compliance program.
5. Cost and time savings
By streamlining processes, eliminating redundant work, and automating manual tasks, Thoropass significantly reduces the time and cost associated with ISO 27001 compliance. Our customers typically see substantial reductions in audit preparation time and resource requirements. The platform’s efficiency means your team can focus on strategic security initiatives rather than getting bogged down in audit administration.
Real-time monitoring and automated alerts help prevent issues before they become costly problems. By surfacing potential issues in advance, the platform helps reduce last-minute surprises and supports more efficient remediation efforts before your audit begins. The platform’s structured approach to evidence collection and management means you’re always audit-ready, eliminating the mad rush and associated costs of last-minute audit preparation.
Conclusion: Take the pain out of ISO 27001 audits
!SO 27001 audits don’t have to be a perpetual drain on your resources. While your competitors continue struggling with manual processes and endless audit cycles, forward-thinking organizations are breaking free from traditional approaches. Thoropass customers have reported reducing audit preparation time by up to 50%, based on internal case studies and customer feedback.
Consider this: What could your team accomplish if they weren’t constantly caught in the audit preparation cycle? How much more strategic value could you deliver if your compliance processes ran smoothly in the background, powered by automation and guided by experts? The endless cycle of audit pain isn’t inevitable – it’s just a sign that your compliance processes haven’t kept pace with your enterprise’s growth.
Ready to break free from the endless audit cycle? Request a demo of Thoropass today and discover how enterprise compliance can be simplified, streamlined, and scaled.
CASE STUDY
ISO 27001 and SOC 2 in less than a year
CoEnterprise achieves multiframework compliance and saves 75% of time on security questionnaires.
Frequently asked questions
An ISO 27001 audit is a systematic evaluation of an organization’s information security management system to determine whether it meets the standard’s requirements. The audit examines how well an organization protects its information assets through appropriate controls and risk management processes.
During the audit process, certified auditors from accredited certification bodies review documentation, interview staff, and examine evidence to verify compliance with the standard’s requirements. This includes evaluating both the design and operational effectiveness of security controls.
To achieve and maintain ISO 27001 certification, organizations must undergo several types of audits. Each plays a critical role in ensuring your information security management system (ISMS) is effective and compliant with ISO standards.
Internal audits
The internal audit process is conducted by your organization to assess the ISMS’s alignment with ISO 27001 requirements. It’s a proactive measure to identify gaps and improve before external assessments.
- An internal audit program involves scheduled reviews of ISMS processes
- Audit findings are documented in an audit report, highlighting areas for improvement
- Internal audits ensure your organization is prepared for external evaluations
External audits
External audits are performed by third-party certification bodies to evaluate your ISMS against ISO 27001 standards. These audits determine whether your organization can achieve or maintain certification.
Yes, ISO 27001 explicitly requires organizations to conduct internal audits at planned intervals. The standard mandates establishing and maintaining an internal audit program to verify that your information security controls and processes meet ISO 27001 requirements and your organization’s objectives.
These internal audits must be conducted by competent and objective internal auditors who understand ISO 27001 requirements and can provide unbiased assessments. The results of these audits, documented in an audit report, feed into the management review process and help drive continuous improvement of your security program.
ISO 27001 certification has historically involved an in-person audit process performed by an ISO 27001 certification body, but remote audits are becoming more common.
However, with remote work more common, ISO 27001 audits can proceed via videoconferencing. If the ISMS design is found to be sufficient, the second stage can commence. Otherwise, the company must remediate any nonconformities in a reasonable amount of time to avoid re-doing the first stage.
The second stage examines the controls and requirements and can similarly take place over a video conference. This typically lasts about twice as long as the stage one audit.
The ISO 27001 audit report will be authored after completion of the audit and passed to the certification body for review.
Because ISO 27001 is a fairly rigid framework, you’ll likely need expert guidance on scaling your controls as your business grows. We get that. Contact our team with questions, comments, or concerns as you tackle the ISO 27001 process!
Only ISO 27001-certified auditors can examine your framework, and only a certification body can issue the final certification. This differs significantly from SOC 2, which any CPA can perform. To qualify, an ISO 27001 auditor must work with a certification body and complete a specified number of audits and hours of training.
When conducting an ISO 27001 audit, organizations may encounter several types of nonconformities that require attention. Let’s examine each type and their implications:
- Major nonconformities: These represent significant failures in your information security management system that could compromise your certification. Common examples include missing mandatory documented procedures, failure to conduct the required risk assessment, or significant gaps in security control implementation. Major nonconformities must be addressed and verified by your external auditor before certification can be granted.
- Minor nonconformities: These are less severe issues that don’t immediately threaten your ISO 27001 certification but still require attention. Examples include incomplete records, inconsistent documentation, or partial implementation of security controls. Organizations typically have time to address these during their regular audit process.
- Continuous improvement: Beyond addressing nonconformities, ISO 27001 emphasizes ongoing improvement of your ISMS. This involves regular monitoring, measurement, and enhancement of security controls based on audit findings and operational experience. Organizations should maintain a structured approach to implementing improvements and tracking their effectiveness.
An ISO 27001 audit policy outlines the framework for how an organization will conduct audits of its information security management system. This policy typically defines the scope, frequency, and methodology for both internal audit and external audits.
The policy should establish clear guidelines for selecting and training your audit team, determining audit criteria, scheduling periodic audits, and reporting findings to management. It serves as a crucial document for maintaining consistency in your audit process and ensuring compliance with ISO 27001 requirements.
The ISO 27001 right to audit refers to an organization’s authority to conduct audits of its suppliers, vendors, or third parties that have access to, or impact on, its information security. This right is typically established through contractual agreements and helps organizations maintain control over their extended security ecosystem.
Organizations should include right-to-audit clauses in their contracts with key suppliers, allowing them to verify that third parties meet required security standards through periodic audits or assessments.
Many organizations still approach security audits as periodic, reactive events rather than opportunities to strengthen their overall security posture.
But organizations face increasing pressure to demonstrate robust, ongoing security and compliance practices. Data breaches cost businesses an average of $4.88 million in 2024 alone (IBM), making security compliance not just a regulatory requirement but a critical business imperative.
This reactive mindset creates significant challenges: Resource drain, operational disruption, unexpected costs, and compliance gaps. By taking a proactive approach to audit readiness, organizations can transform compliance from a burdensome exercise into a strategic advantage.
Key takeaways
- Audit readiness can become a strategic capability that contributes to business value beyond satisfying compliance obligations
- Organizations with mature audit readiness programs tend to spend less time on security audit preparation and experience fewer findings
- A well-structured maturity model helps organizations benchmark their current state and develop a roadmap for improvement
- Thoropass’ purpose-built platform enables multi-framework compliance that can reduce manual effort through shared framework requirements
What are the costs of poor audit readiness?
Many organizations underestimate the full impact of approaching security audits reactively. While the direct costs of compliance audits are easily quantifiable, the hidden costs of unpreparedness are often much higher than initially expected. Organizations operating across multiple compliance frameworks face compounding financial strain as these costs multiply with each additional security and IT audit, creating a cascade of unexpected expenses that impact the bottom line.
Resource allocation and productivity impacts
Beyond direct financial implications, unprepared organizations suffer significant resource allocation challenges and productivity disruptions. Regular audit fire drills—the frantic scramble to collect evidence, document processes, and prepare stakeholders—divert key personnel from strategic initiatives and daily operations.
Reputational risks of audit failures
The reputational damage from audit unpreparedness can be equally devastating. Failed security audits or qualified opinions must be disclosed to stakeholders, eroding customer and partner confidence at critical moments. Organizations may find themselves unable to close deals or enter new markets due to compliance gaps, creating competitive disadvantages that persist long after the audit cycle concludes.
Regulatory penalties and business restrictions
Regulatory frameworks continue evolving with increasingly substantial penalties for non-compliance. GDPR violations, for example, can result in fines up to €20 million or 4% of global revenue, while HIPAA penalties can reach $1.5 million per violation category per year.
Industry-specific regulations often include penalties beyond monetary fines, including operational restrictions that fundamentally impact business models. These penalties represent just the direct regulatory consequences—without considering the broader business impact of urgent remediation requirements that follow.
Operational disruption during audits
Perhaps most significantly, unprepared organizations experience substantial business continuity disruptions during audit periods. Feature releases and product updates get delayed to stabilize audit environments, sales and customer onboarding processes pause pending audit completion, and strategic initiatives defer as key personnel focus exclusively on audit activities.
This organizational paralysis can last weeks or months, with executive attention diverted from growth activities to compliance firefighting. The cumulative effect transforms what should be a structured validation process into an existential business crisis—clearly demonstrating why audit readiness must be considered a strategic capability rather than merely a periodic compliance activity.
How do you measure audit readiness maturity?
To help organizations benchmark their current state and develop a strategic roadmap for improvement, we’ve developed a five-level maturity model for audit readiness:
Level 1: Reactive (ad-hoc, audit-driven approach)
Organizations at this level typically display a reactive approach that makes it difficult to scale compliance programs as the organization grows:
- Security audit preparation begins only when the next audit is imminent
- Evidence collection is manual and often incomplete
- Documentation is created specifically for audits rather than maintained continuously
- Key stakeholders are unprepared for auditor interviews
- No standardized approach exists across compliance frameworks
- Significant findings are common, and remediation is reactive
Level 2: Proactive (established processes, dedicated resources)
While still maturing, these organizations experience more consistent results and reduced audit fatigue compared to Level 1 organizations:
- Dedicated resources to ensure compliance, with clear responsibilities
- Documented policies and procedures that align with key frameworks
- Basic evidence-collection processes that operate outside audit cycles
- Preliminary control mapping across multiple frameworks
- Improved stakeholder preparation through training and documentation
- More predictable audit outcomes with fewer critical findings
Level 3: Integrated (cross-functional collaboration, technology enablement)
These organizations view compliance as a continuous program rather than a series of point-in-time assessments, demonstrating more sophisticated capabilities:
- Cross-functional compliance committees with executive sponsorship
- Technology-enabled evidence collection and documentation
- Integrated control frameworks that align with business processes
- Ongoing compliance monitoring between formal audit cycles
- Regular stakeholder communication and training programs
- Significantly reduced security audit preparation time and resource requirements
Level 4: Strategic (continuous compliance monitoring, business alignment)
These organizations leverage compliance as a competitive advantage—demonstrating security maturity to customers and partners while minimizing internal disruption:
- Continuous control monitoring with real-time compliance dashboards
- Automated evidence collection integrated with business systems
- Proactive identification and remediation of control gaps
- Compliance considerations embedded in product and system design
- Metrics-driven approach to compliance program effectiveness
- Security audits become validation exercises rather than discovery processes
Level 5: Transformative (compliance as a competitive advantage)
At this level, security audit readiness becomes a strategic differentiator that delivers measurable business value beyond just satisfying compliance requirements. It includes:
- Predictive tools that help anticipate changes in compliance obligations or qualify as roadmap/vision.
- Integrated security and compliance ecosystem with minimal redundancy
- Compliance frameworks that accelerate rather than impede business growth
- Evidence collection and validation as a byproduct of normal operations
- Industry leadership in compliance methodologies and practices
- Audit processes that reflect a mature and well-integrated security and compliance posture
What are the essential elements of audit readiness?
Regardless of current maturity level, organizations can strengthen their audit readiness by focusing on these six core elements:
1. Governance structure and clear accountability
Effective security audit readiness starts with well-defined governance:
- Executive-sponsored compliance committee with cross-functional representation
- Clearly documented roles and responsibilities for compliance activities
- Designated compliance owners for each control domain
- Accountability metrics tied to performance objectives
- Regular governance meetings to assess program effectiveness
This governance framework ensures appropriate visibility, resource allocation, and accountability throughout the compliance lifecycle.
2. Risk assessment methodologies
A structured approach to risk assessment forms the foundation for targeted compliance efforts:
- Documented methodology for identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks
- Regular risk assessment cycles aligned with business changes
- The clear connection between identified risks and implemented controls
- Risk registers that inform audit scoping and control prioritization
- Alignment between business risk tolerance and compliance objectives
By understanding the relationship between risks and controls, organizations can focus resources on high-impact areas rather than treating all controls equally.
3. Evidence management and documentation strategy
Efficient evidence management significantly reduces audit effort:
- Centralized evidence repository with appropriate access controls
- Evidence-collection processes integrated into business operations
- Clear naming conventions and metadata to make everything easily accessible
- Evidence retention policies aligned with compliance requirements
- Automated evidence collection where possible to reduce manual effort
This structured approach ensures that evidence is readily available when needed rather than requiring last-minute collection efforts.
4. Control optimization and automation
Mature organizations continuously refine their control environment:
- Regular assessment of control effectiveness and efficiency
- Elimination of duplicate or redundant controls
- Automation of control execution and evidence collection
- Clear control descriptions that align with framework requirements
- Balanced preventive, detective, and corrective control types
This optimization reduces compliance burden while improving security posture—a win-win for both operational efficiency and risk management.
5. Cross-functional collaboration protocols
Security audit readiness extends beyond the compliance team:
- Documented protocols for cross-functional collaboration
- Regular touchpoints with key control owners and stakeholders
- Shared compliance calendars and milestone tracking
- Clear escalation paths for compliance issues
- Joint accountability for compliance outcomes
These collaboration mechanisms ensure that compliance remains integrated with business operations rather than becoming an isolated function.
6. Stakeholder communication plan
Effective communication significantly improves audit outcomes:
- Standardized communication templates for different stakeholder groups
- Regular updates on compliance program status and upcoming activities
- Targeted preparation for stakeholders participating in auditor interviews
- Clear communication of findings and remediation requirements
- Executive-level reporting on compliance program effectiveness
This structured communication approach ensures that stakeholders understand their roles and remain engaged throughout the compliance lifecycle.
How does technology transform audit readiness?
Technology plays an increasingly critical role in scaling audit readiness programs as organizations grow and compliance requirements expand.
Manual to automated compliance evolution
The evolution from manual to automated compliance processes follows a predictable pattern:
- Manual processes: Spreadsheets, shared drives, and email-based evidence collection
- Basic automation: Simple workflow tools and document management systems
- Dedicated solutions: Purpose-built compliance platforms with framework-specific capabilities
- Integrated ecosystems: Compliance solutions that connect with business systems for automated evidence collection
- Intelligent compliance: AI-enhanced solutions that provide predictive insights and continuous monitoring
This progression significantly reduces manual effort while improving accuracy and consistency—allowing compliance teams to focus on strategic activities rather than administrative tasks.
Thoropass’ purpose-built platform fits into this evolution by providing dedicated compliance capabilities that eliminate the inefficiencies of manual processes while offering more sophisticated features than basic workflow tools.
Centralized evidence management benefits
A centralized evidence repository delivers multiple benefits:
- Single source of truth for compliance artifacts
- Reduced duplication of evidence-collection efforts
- Improved version control and change tracking
- Streamlined access for auditors during fieldwork
- Simplified evidence mapping across multiple frameworks
Organizations with centralized repositories report a significant reduction in evidence collection effort compared to decentralized approaches. Thoropass‘ centralized evidence repository is specifically designed to solve one of the most time-consuming aspects of security audit preparation—gathering, organizing, and mapping evidence across multiple frameworks to break free from endless audit loops.
Continuous monitoring capabilities and real-time compliance status
Modern compliance platforms provide visibility beyond point-in-time assessments:
- Real-time dashboards showing control status and exceptions
- Automated testing of control effectiveness
- Continuous validation of critical security configurations
- Early warning of potential compliance gaps
- Trend analysis to identify emerging issues
This continuous visibility allows organizations to address compliance gaps proactively rather than discovering them during audits.
Analytics and predictive insights for proactive risk management
Advanced compliance solutions leverage analytics to deliver strategic insights:
- Identification of control patterns and potential weaknesses
- Predictive analysis of likely audit findings
- Resource optimization recommendations
- Benchmarking against industry compliance standards
- ROI analysis for compliance investments
These insights transform compliance data into actionable intelligence that supports strategic decision-making.
Integration with broader risk management systems
Mature organizations integrate compliance with enterprise risk management using:
- Unified risk and compliance taxonomies
- Integrated assessment methodologies
- Coordinated control testing and validation
- Shared reporting and dashboards
- Aligned governance structures
This integration ensures that compliance activities support broader risk management objectives rather than operating in isolation.
Multi-framework control mapping
Effective control mapping provides significant efficiency gains:
- Identification of common requirements across frameworks
- Unified control descriptions that satisfy multiple standards
- Gap analysis to identify framework-specific controls
- Rationalized control set that minimizes duplication
- Clear visibility into cross-framework coverage
This mapping allows organizations to implement once and comply many times—significantly reducing the overhead of multi-framework compliance.
Cross-framework evidence optimization
With proper planning, a single piece of evidence can often satisfy requirements across multiple frameworks:
- Standardized evidence formats that meet multiple framework expectations
- Consolidated evidence requests to minimize stakeholder burden
- Cross-linking of evidence to applicable controls across frameworks
- Centralized evidence repository with framework-specific views
- Efficient reuse of evidence across multiple audits
This unified approach can reduce the evidence-collection effort compared to framework-specific collection processes.
Multi-certification audit strategies
Advanced organizations structure their audit programs to maximize efficiency:
- Coordinated audit timing to support multiple frameworks
- Integrated audit scoping that covers all relevant requirements
- Selection of auditors with multi-framework capabilities
- Unified sampling methodologies that satisfy multiple standards
- Consolidated audit interviews that address cross-framework topics
This strategic approach reduces duplicative audit activities while still satisfying the unique requirements of each framework.
How do you build effective auditor relationships?
The relationship between organizations and their auditors fundamentally shapes the compliance process. Selecting the right security audit partner means finding a firm that understands your industry context, compliance objectives, and organizational culture.
Successful organizations have moved beyond engaging with auditors only during formal assessment periods. Instead:
- They establish year-round communication channels that transform the traditional adversarial dynamic into a strategic partnership.
- Regular check-ins provide opportunities to discuss significant changes, address emerging compliance challenges, and align on framework interpretations before they become audit issues.
This ongoing dialogue eliminates surprises and allows both parties to solve problems collaboratively rather than through formal findings.
The audit planning process presents a critical opportunity to optimize the assessment experience. Forward-thinking organizations engage in collaborative scoping that focuses auditor attention on the most relevant risk areas. This approach includes:
- Jointly developing audit scopes
- Agreeing on sampling methodologies
- Coordinating timing to minimize business disruption
The most effective audit relationships feature clear evidence expectations from the beginning—ensuring that both parties work toward the same objectives with minimal wasted effort.
Transparency represents perhaps the most counterintuitive element of modern audit relationships. Honest acknowledgment of known gaps—accompanied by thoughtful remediation plans—builds trust and ultimately leads to more efficient assessments.
Conclusion: Audit readiness as a strategic advantage
Audit readiness has evolved from a tactical compliance activity into a strategic business capability. Organizations that develop mature security audit readiness capabilities realize significant benefits:
- Reduced compliance costs through improved efficiency
- Minimized business disruption during audit cycles
- Enhanced security posture through continuous monitoring
- Improved stakeholder confidence in compliance outcomes
- Competitive differentiation in security-conscious markets
By adopting the maturity model and key elements outlined in this article, organizations can transform their approach to compliance—moving from reactive scrambling to strategic readiness that delivers measurable business value.
As regulatory complexity continues to increase, this strategic approach to audit readiness will become increasingly critical—not just for compliance success but also for overall business performance and resilience.
Ready to transform your compliance approach? Partner with Thoropass to implement a purpose-built platform that streamlines evidence collection, breaks free from endless audit loops, and enables multi-framework compliance with significantly reduced effort. Learn how our experienced experts can help you turn audit readiness into a strategic advantage.
GUIDE
Closing the audit gap: A guide for infosec leaders
Thoropass has once again been named a Leader in G2’s Spring 2025 Grid Reports across multiple categories! While the badges provide welcome recognition, what truly energizes us is the validation from our users that we’re delivering on our mission: modernizing and simplifying compliance and audit for businesses of all sizes.
Our mission continues to be transforming how companies approach compliance. Let’s explore the key areas where Thoropass is making a significant impact this spring:
Leader in the Audit Management Category
Thoropass has earned Leader Badge status in the following reports for Audit Management:
- EMEA Regional Grid® Report for Audit Management | Spring 2025
- Momentum Grid® Report for Audit Management | Spring 2025
- Mid-Market Grid® Report for Audit Management | Spring 2025
- Grid® Report for Audit Management | Spring 2025
About the Audit Management Category
Audit Management software helps companies streamline their audit processes and comply with regulations or internal policies. Used across heavily regulated industries, these tools enable compliance professionals and operations managers to efficiently schedule, implement, and analyze audit results.
Leader in the Cloud Compliance Category
Thoropass is proud to achieve Leader Badge Status for Cloud Compliance in:
- Momentum Grid® Report for Cloud Compliance | Spring 2025
- Small-Business Grid® Report for Cloud Compliance | Spring 2025
About the Cloud Compliance Category
Cloud Compliance software ensures regulatory standards and provides controls for networks and cloud infrastructure. These tools improve visibility over cloud workloads and network flows, offering continuous protection against threats like server malware and network intrusion.
Leader in the Cloud Security Category
Thoropass has been recognized as a Leader in:
- Small-Business Grid® Report for Cloud Security | Spring 2025
- Grid® Report for Cloud Security | Spring 2025
About the Cloud Security Category
Cloud Security software protects organizations’ cloud infrastructure and assets from threats and vulnerabilities. These solutions provide visibility, monitoring, and control over cloud resources to ensure data protection and security compliance.
Leader in the Governance, Risk, & Compliance Category
Thoropass is thrilled to receive Leader Badge status in:
- EMEA Regional Grid® Report for Governance, Risk & Compliance | Spring 2025
- Grid® Report for Governance, Risk & Compliance | Spring 2025
About the Governance, Risk, and Compliance Category
GRC software aligns IT with business objectives while effectively managing risk and compliance requirements. It helps companies establish governance frameworks, identify and mitigate risks, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Leader in the Security Compliance Category
Thoropass has achieved Leader Badge Status in:
- Momentum Grid® Report for Security Compliance | Spring 2025
- Grid® Report for Security Compliance | Spring 2025
- Small-Business Grid® Report for Security Compliance | Spring 2025
About the Security Compliance Category
Security Compliance software streamlines documentation and management of cybersecurity frameworks for audits. These tools help teams assess and document compliance across standards like SOC 2, PCI DSS, ISO 27001, and NIST frameworks.
Leader in the Vendor Security & Privacy Assessment Category
Thoropass is pleased to be named a Leader in:
- Momentum Grid® Report for Vendor Security and Privacy Assessment | Spring 2025
- Grid® Report for Vendor Security and Privacy Assessment | Spring 2025
About Vendor Security and Privacy Assessment
Vendor Security and Privacy Assessment software helps companies manage risk assessment processes when evaluating vendors and third parties. It enables businesses to understand cybersecurity and privacy risks associated with current and prospective business relationships.
Customer success drives our success
None of these recognitions would be possible without our incredible customers who’ve taken the time to share their experiences on G2. Your feedback doesn’t just earn us badges—it drives our innovation, shapes our roadmap, and fuels our passion to keep making compliance simpler and more strategic for businesses everywhere.
We’re genuinely honored by your trust and inspired by your success stories. Every time you tell us how Thoropass has transformed your compliance journey from overwhelming to empowering, it reinforces why we do what we do.
Ready to experience award-winning compliance?
If you’re looking to join the ranks of satisfied Thoropass users who are modernizing their approach to compliance and audit, we’d love to show you how. From automating evidence collection to streamlining audits, discover why our users consistently rate us as a leader in the industry.
Talk to us today and see firsthand how we can help you transform compliance into a business advantage.
Payment security compliance has evolved far beyond an annual checkbox exercise. Organizations face mounting pressure to protect cardholder data across increasingly complex technology stacks, while simultaneously managing multiple compliance frameworks and responding to evolving threats. This expanding scope, combined with traditional manual audit processes, has led to a phenomenon many enterprises know too well: audit fatigue.
The transition to PCI DSS v4.0, published in March 2022, marks a pivotal shift in payment security compliance. With PCI DSS v3.2.1 now retired (as of March 31, 2024), v4.0 is the current standard. Organizations are working toward the next critical deadline of March 31, 2025, when all requirements initially labeled as ‘best practices’ in v4.0 will become mandatory.
Beyond strengthening security requirements around authentication, encryption, and access controls, v4.0 introduces new opportunities for organizations to modernize their compliance programs as historically ‘best practices’ will now become requirements. Rather than viewing these changes as another layer of complexity, forward-thinking enterprises are leveraging this transition to transform their audit processes—especially given the new customized approach options that enable organizations to demonstrate security objectives through alternative controls.
The key lies in shifting from periodic compliance exercises to continuous security validation. By adopting modern approaches to PCI DSS audits—through automation, framework harmonization, and real-time monitoring—organizations can break free from the resource-intensive cycle of point-in-time assessments. This transformation streamlines the audit process and delivers tangible business value through improved security posture, reduced costs, and more predictable compliance outcomes.
Key takeaways
- Transform your PCI DSS audit process by shifting from periodic assessments to continuous validation—aligning with meeting the new mandatory requirements of v4.0 while reducing resource drain and audit fatigue through automated evidence collection and real-time control monitoring.
- Leverage technology to harmonize compliance workflows across frameworks, eliminating redundant documentation through intelligent control mapping between PCI DSS v4.0, SOC 2, and ISO 27001—enabling efficient, parallel certifications that reduce costs and timeline uncertainty.
- Create a predictable, transparent audit experience by combining purpose-built compliance technology with expert guidance, transforming traditionally unpredictable assessments into streamlined operations that strengthen your security posture.
The stakes of PCI DSS audits
PCI DSS compliance represents far more than a regulatory requirement—it’s a critical business imperative that directly impacts revenue streams, customer trust, and market access. As organizations prepare for PCI DSS v4.0’s enhanced requirements, understanding these stakes becomes even more vital for strategic planning and resource allocation.
Current threat landscape and financial implications
Payment fraud continues to evolve in sophistication and scale, with cybercriminals increasingly targeting enterprise payment infrastructures. The financial impact of non-compliance extends well beyond the immediate costs of potential breaches—which averaged $4.88 million in 2024 (IBM / Ponemon Institute).
Under PCI DSS v4.0, organizations face stricter requirements around authentication, encryption, and access controls, with non-compliance potentially resulting in penalties of up to $100,000 per month. However, the most significant financial risk lies in the operational disruption and customer churn that follows a payment security incident. With v4.0’s emphasis on continuous security validation, enterprises must shift from viewing compliance as an annual expense to treating it as an ongoing operational investment.
Business criticality of payment security
Transaction volume considerations have become increasingly complex as enterprises expand their payment channels and digital transformation initiatives. PCI DSS v4.0 introduces new requirements for securing e-commerce payments and API integrations, making compliance more challenging for organizations processing high transaction volumes across multiple platforms.
The standard’s vendor management requirements have also expanded, requiring more rigorous oversight of Third-Party Service Providers (TPSPs) and their potential impact on cardholder data security. Moreover, market access implications have intensified—many enterprise customers and partners now require proof of PCI DSS compliance before engaging in business relationships, making it a de facto prerequisite for market participation rather than just a regulatory obligation.
Modern PCI DSS audit challenges
As enterprises prepare for PCI DSS v4.0 implementation, longstanding audit challenges are becoming even more pronounced. The traditional approach to compliance—characterized by manual processes and point-in-time assessments—is increasingly unsustainable for organizations managing complex security requirements across multiple frameworks.
Key challenges facing enterprises include:
- Framework overlap: Managing PCI DSS alongside SOC 2, ISO 27001, and other frameworks leads to duplicated efforts and fragmented evidence collection, particularly as v4.0 introduces new controls that further intersect with existing frameworks.
- Resource intensity: Manual evidence collection and documentation consume significant team resources, with compliance managers spending a substantial percentage of their time on administrative tasks rather than strategic security initiatives.
- Process inefficiency: Repetitive audit cycles and redundant work continuously drain resources, exacerbated by siloed approaches to framework-specific compliance requirements.
- Cost unpredictability: Hidden expenses and scope creep emerge throughout the audit lifecycle, from unexpected remediation requirements to extended audit timeframes and additional assessor fees.
- Stakeholder coordination: Managing communication between auditors, technical teams, and leadership becomes increasingly complex under v4.0’s expanded requirements for documentation and evidence of continuous compliance.
- Continuous validation: Moving beyond point-in-time assessments to meet v4.0’s emphasis on ongoing security validation requires a fundamental shift in how organizations approach compliance monitoring and documentation.
Why traditional audit approaches fall short
Traditional approaches to PCI DSS compliance—built around annual assessments and manual processes—are increasingly misaligned with both modern enterprise needs and v4.0’s enhanced requirements for continuous security validation.
These legacy methods create systemic inefficiencies that compound compliance challenges.
Key limitations of traditional approaches include:
- Manual documentation burden: The reliance on spreadsheets and email chains for evidence collection creates visibility gaps and version control issues, leading to missed tasks and endless back-and-forth with auditors and stakeholders.
- Framework silos: Traditional methods treat each compliance framework as a separate initiative, resulting in duplicate evidence collection and missed opportunities to leverage controls across standards like PCI DSS, SOC 2, and ISO 27001.
- Limited visibility: Poor communication channels between organizations and Qualified Security Assessors (QSAs) create unnecessary audit loops and extend assessment timelines, particularly problematic as v4.0 requires more detailed evidence of continuous compliance.
- Resource drain: Compliance teams spend excessive time on administrative tasks rather than strategic security initiatives, with technical resources pulled into repetitive documentation requests rather than focused on security improvements.
- Reactive posture: Point-in-time assessments create a reactive approach to security requirements, making it difficult to maintain continuous compliance or adapt to emerging threats between audit cycles.
Five steps to a smoother PCI DSS audit process
As enterprises prepare for PCI DSS v4.0, leading organizations are moving from traditional audit approaches to more strategic, technology-enabled compliance programs. Modernizing your audit process with these five key elements allows you to transform compliance from an annual burden into a streamlined, predictable operation that delivers continuous security validation.
1. Continuous control monitoring
Modern compliance demands real-time visibility into your security controls. Traditional point-in-time assessments no longer suffice, especially under PCI DSS v4.0’s enhanced requirements for ongoing validation. Continuous control monitoring enables your organization to proactively identify and address potential compliance gaps, rather than scrambling to remediate issues during audit cycles.
Organizations that excel at continuous monitoring typically employ automated tools that track control effectiveness across frameworks, providing real-time dashboards and alerts when controls drift from their desired state. This approach not only satisfies PCI DSS requirements but also strengthens your overall security posture by enabling rapid response to emerging risks.
2. Automated evidence collection
Manual evidence collection represents one of the biggest drains on compliance team resources. By automating this process, enterprises can significantly reduce the time spent gathering and organizing documentation while improving accuracy and completeness.
Modern compliance platforms can automatically collect evidence from various systems and cloud services, maintaining a continuously updated repository of compliance artifacts. This automation eliminates the traditional scramble to gather evidence during audit cycles and ensures that your documentation remains current and readily available for assessor review.
3. Cross-framework mapping
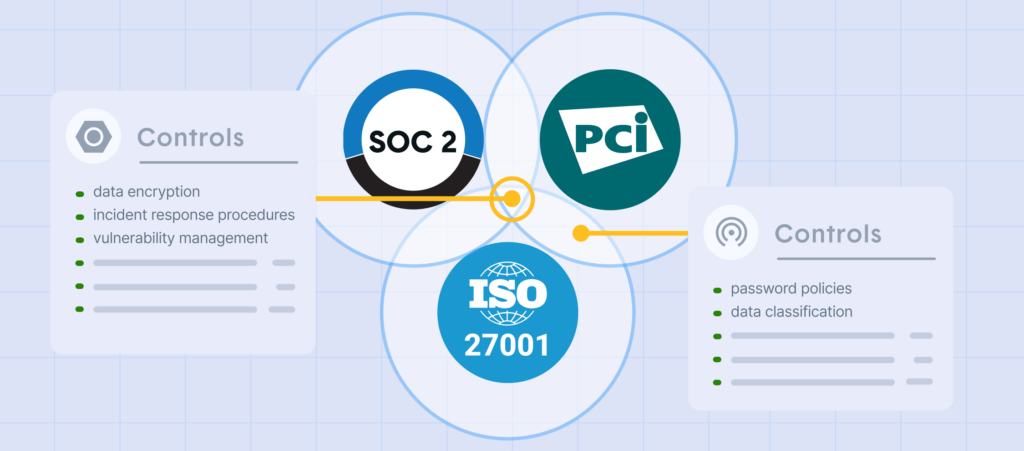
As enterprises manage multiple compliance frameworks, the ability to leverage controls across standards becomes crucial. Intelligent control mapping allows organizations to satisfy requirements for PCI DSS, SOC 2, ISO 27001, and other frameworks simultaneously, eliminating redundant work.
By mapping controls once and applying them across frameworks, organizations can reduce audit fatigue and create a more efficient compliance program. This approach is particularly valuable as organizations prepare for PCI DSS v4.0, as many of its new requirements align with controls already in place for other frameworks.
For example:
- PCI DSS v4.0’s enhanced requirements for access control and authentication align closely with SOC 2 CC6.1 (Logical Access Security) and ISO 27001 A.9 (Access Control).
- Similarly, v4.0’s new requirements for security awareness training map directly to SOC 2 CC2.2 (Security Commitments) and ISO 27001 A.7.2.2 (Information Security Awareness). Organizations can leverage existing controls and evidence for these overlapping requirements, significantly reducing documentation burden and assessment time.
4. Unified compliance platform
A unified platform approach eliminates the fragmentation that often plagues compliance programs. Rather than managing multiple tools, spreadsheets, and communication channels, organizations can centralize their compliance operations in a single, purpose-built environment.
This centralization creates a single source of truth for compliance data, streamlines stakeholder communication, and provides clear visibility into audit progress and potential bottlenecks. The right platform will support both current compliance needs and future framework additions, scaling alongside your organization’s evolving requirements.
5. QSA collaboration
Effective collaboration with Qualified Security Assessors (QSAs) can significantly impact audit efficiency. Modern approaches facilitate transparent, ongoing communication between your team and assessors, replacing the traditional pattern of lengthy audit cycles and repeated evidence requests.
By establishing clear communication channels and maintaining continuous dialogue with QSAs, organizations can resolve questions quickly, address potential issues proactively, and maintain momentum throughout the audit process. This collaborative approach, supported by technology, helps eliminate audit loops and ensures more predictable timelines and outcomes.
The Thoropass advantage for PCI DSS audits
As enterprises prepare for PCI DSS v4.0, choosing a compliance partner becomes increasingly critical. Thoropass delivers a modern approach to payment security compliance that combines purpose-built technology with deep compliance expertise, enabling organizations to transform their audit experience from an unpredictable burden into a streamlined, strategic process.
- Purpose-built platform: Unlike legacy compliance tools cobbled together from generic project management software, Thoropass’s platform is engineered specifically for complex enterprise compliance needs. Our unified environment eliminates the fragmentation of traditional approaches, providing clear visibility into audit progress and automated evidence collection that reduces manual documentation burden.
- Multi-framework efficiency: Thoropass’s intelligent control mapping enables organizations to leverage a single evidence repository across PCI DSS, SOC 2, ISO 27001, and other frameworks. This approach eliminates redundant documentation and allows enterprises to achieve multiple certifications through streamlined, parallel assessments—as demonstrated by clients like Forage, who successfully completed both PCI DSS and SOC 2 certifications while saving over $100,000 in development costs.
- Expert support: Beyond technology, Thoropass offers guidance throughout the audit lifecycle from compliance experts who understand the technical requirements and strategic implications of payment security compliance. Our team works alongside yours to optimize audit scope, streamline evidence collection, and ensure predictable outcomes.
- Predictable timeline: Thoropass delivers a structured approach that significantly reduces audit cycles by eliminating common audit bottlenecks through automated evidence collection, intelligent control mapping, and streamlined QSA collaboration. Organizations can move from uncertain timelines to predictable, efficient assessments that maintain continuous compliance.
- Cost control: Traditional audit approaches often incur hidden costs through extended timelines, repeated evidence requests, and redundant work across frameworks. Thoropass’s unified approach eliminates these inefficiencies, providing transparent pricing and demonstrable cost savings through automation and framework harmonization.
Transform your PCI DSS audit experience today. Schedule a demo to see how Thoropass can streamline your compliance program, reduce audit complexity, and deliver predictable, efficient outcomes as you prepare for PCI DSS v4.0.
CASE STUDY
Forage streamlined SOC 2 and PCI audits simultaneously to achieve $100k in savings
Utilizing Thoropass’ multi-framework, single-audit approach, Forage was able to beat their compliance deadlines and save 3-6 months of development time.
Frequently Asked Questions
A PCI DSS audit is a comprehensive assessment conducted to verify an organization’s compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which is established by the PCI Security Standards Council. This evaluation examines how well an organization protects cardholder data and maintains secure systems throughout its payment processing environment. The audit process involves reviewing security controls, policies, and procedures to ensure they meet the standard’s requirements for safeguarding sensitive data.
During the audit, a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) thoroughly examines an organization’s cardholder data environment, including network resources, system components, and security systems. The assessment covers all 12 PCI DSS requirements, from maintaining secure networks to implementing strong access control measures. Organizations must demonstrate that they have implemented required controls, regularly test security systems, and maintain compliance through continuous monitoring.
Any organization that stores, processes, or transmits payment card data must comply with PCI DSS requirements, though the specific audit requirements vary based on transaction volume and merchant level.
Level 1 merchants—those processing over 6 million card transactions annually across all channels or those that have experienced a data breach—must undergo an annual PCI compliance audit conducted by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA). Additionally, any organization serving as a Third-Party Service Provider (TPSP) to these Level 1 merchants typically requires a formal audit to demonstrate data security competence.
For other merchant levels, the requirements differ. Level 2 merchants (1-6 million transactions annually) may complete a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) and undergo quarterly network scans by Approved Scanning Vendors.
However, many organizations choose to undergo formal audits voluntarily, recognizing that robust security validation through a formal PCI DSS audit helps protect cardholder data and strengthens their overall security posture. This is particularly true for enterprises managing complex payment ecosystems or those seeking to establish strong security credentials with partners and customers.
A Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) is a professional certified by the PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) to conduct comprehensive PCI DSS audits. QSAs perform thorough assessments of an organization’s cardholder data environment, evaluate security controls, and validate compliance through detailed testing procedures. They are authorized to provide formal attestations of compliance and typically work with larger enterprises or organizations requiring rigorous third-party validation.
The Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ), on the other hand, is a validation tool for organizations to conduct their own PCI DSS assessments. There are different SAQ types based on how an organization handles credit card data and sensitive authentication data. While SAQs can be appropriate for smaller organizations or those with simpler payment environments, they generally don’t provide the same level of validation as a QSA assessment. Many enterprises choose QSA assessments even when eligible for SAQ because they offer more robust validation, better align with multi-framework compliance strategies, and provide stronger assurance to stakeholders.
The cost of a PCI DSS audit varies significantly based on several strategic factors within your organization’s compliance ecosystem. Key considerations include:
-
- The scope and complexity of your cardholder data environment
-
- The number of system components requiring assessment
-
- Whether you maintain secure systems across multiple locations or cloud environments.
Organizations must also consider the broader context of their compliance program, including how PCI DSS requirements align with other frameworks like SOC 2 or ISO 27001.
A comprehensive cost analysis should account for both direct and indirect factors: the complexity of your risk assessment processes, the maturity of your security controls, the need for gap analysis prior to formal auditing, and your organization’s approach to maintaining PCI DSS compliance through continuous monitoring.
Rather than viewing PCI compliance as a standalone cost center, forward-thinking organizations evaluate audit investments within their broader security and compliance strategy. Contact our team to discuss your specific compliance needs and how a modern approach to framework harmonization can help optimize your audit investment.
The duration of a PCI DSS audit varies significantly based on organizational complexity and compliance program maturity. For enterprises managing extensive cardholder data environments, the traditional audit cycle often spans 3-6 months when using conventional methods. However, this timeline can extend considerably if organizations lack automated evidence-collection systems or maintain multiple network resources across different locations.
Key factors influencing audit duration include:
-
- The maturity of your security systems
-
- The effectiveness of your security awareness training programs
-
- How well you regularly test security systems throughout the year
Organizations that implement strong access control measures and maintain continuous compliance monitoring typically experience more predictable and efficient audit cycles. Modern approaches that leverage automated evidence collection and cross-framework control mapping can significantly streamline the process, particularly for enterprises managing multiple compliance requirements simultaneously.
Consider consulting with a compliance partner who can evaluate your specific environment and help optimize your audit timeline through technology-enabled processes and expert guidance.
While PCI DSS v4.0 introduces enhanced controls and more flexible implementation options, the 12 core requirements remain consistent as the fundamental framework for payment security. These requirements, established by the PCI Security Standards Council, continue to serve as the blueprint for protecting cardholder data and maintaining secure systems. However, specific implementation details and validation procedures have evolved to address emerging threats and technologies.
Install and maintain network security controls:
-
- Install and maintain network security controls (formerly “firewalls”)
- Apply secure configurations to system components and stop using vendor-supplied defaults
Protect account data:
-
- Protect stored cardholder data
- Protect cardholder data with strong cryptography during transmission
Maintain a vulnerability management program:
-
- Protect systems and networks from malware
- Develop and maintain secure systems and software
Implement strong access control measures:
-
- Restrict access to system components and sensitive data
- Identify users and authenticate access to system components
- Restrict physical access to cardholder data
Regularly monitor and test networks:
-
- Log and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data
- Regularly test security systems and processes
Maintain an information security policy:
12. Support information security with organizational policies and program
The frequency of PCI DSS audits depends primarily on your organization’s merchant level and transaction volume, though many enterprises opt for more frequent assessments to maintain continuous compliance.
Level 1 merchants—those processing over 6 million transactions annually or who have experienced a data breach—must undergo annual assessments by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) and conduct quarterly network scans using Approved Scanning Vendors. These requirements reflect the PCI Security Standards Council’s emphasis on continuous validation, particularly as organizations transition to PCI DSS v4.0.
However, viewing PCI compliance as an annual or quarterly event no longer aligns with modern security demands. Forward-thinking organizations are shifting toward continuous monitoring approaches that integrate with their broader security strategy. This involves regularly testing security systems, conducting ongoing risk assessments, and maintaining secure systems through automated control monitoring.
This approach satisfies compliance requirements, strengthens your overall security posture, and reduces the resource intensity of formal audit cycles. Many enterprises find that implementing continuous monitoring technologies and automated evidence-collection systems helps transform compliance from periodic assessments into a more predictable, ongoing program.
For enterprise compliance leaders, the data security audit process has become an endless loop of spreadsheets, status meetings, and evidence requests. What should be a strategic initiative to protect your organization has devolved into a resource-draining exercise that keeps your team stuck in reactive mode.
The signs are everywhere: Compliance managers juggling multiple frameworks with redundant evidence requests. IT teams constantly interrupted for screenshots and configurations. Auditors requesting “just one more thing” weeks after you thought you were done. And through it all, the gnawing concern that despite all this effort, something crucial might slip through the cracks.
It’s not just you. Large enterprises across industries are discovering that traditional audit approaches simply cannot scale to meet today’s complex compliance demands. With regulatory requirements multiplying and cyber threats evolving daily, the old way of managing data security audits isn’t just inefficient—it’s becoming a genuine business risk.
But here’s the reality: while the complexity of enterprise data security audits isn’t going away, the painful, manual processes that make them feel overwhelming absolutely can. Leading organizations are transforming their approach to data security audits through integrated frameworks, automated evidence collection, and continuous compliance monitoring. This guide will show you how to break free from audit chaos and build a streamlined, predictable process that scales with your enterprise needs.
Key takeaways
- Traditional audit processes are failing enterprises at scale: Manual evidence collection, siloed teams, and framework-by-framework approaches create unsustainable operational burdens and increase compliance risk.
- Modern platforms with multi-framework capabilities and automated evidence collection can reduce audit cycles by up to 50% while improving accuracy and completeness.
- Leading enterprises are moving beyond point solutions to embrace comprehensive platforms that combine automation, expert guidance, and continuous monitoring—transforming audits from periodic fire drills into streamlined, predictable processes.
The growing importance and complexity of data security audits for enterprises
Today’s enterprises face unprecedented pressure to protect sensitive data while demonstrating compliance across multiple regulatory frameworks. A robust data security audit program isn’t just a checkbox exercise—it’s a strategic imperative for enterprise risk management.
Expanding regulatory landscape
The proliferation of data protection regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA has created a complex web of compliance requirements.
Matt Udicious, Director of InfoSec Assurance at Thoropass states:
These changes reflect the global nature of business and evolving regulatory environments. Enterprises need scalable, intelligent solutions that transform compliance from a challenge into a strategic advantage, helping them navigate this intricate ecosystem efficiently.
Each framework demands specific security controls, documentation, and evidence of continuous monitoring. For enterprises operating across jurisdictions, managing these overlapping requirements without a systematic approach leads to redundant work and increased compliance risk.
Evolving threat environment
The financial impact of data breaches continues to rise, with the average cost now exceeding $4.88 million (IBM). Modern cyber threats—from sophisticated ransomware operations to targeted social engineering attacks—require enterprises to maintain comprehensive visibility into their security posture. Regular security audits provide the structured assessment needed to identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Enterprise infrastructure complexity
Today’s enterprise technology landscape combines legacy systems, cloud services, and distributed workforce tools—each introducing new security considerations. Managing data security across this complex ecosystem requires a systematic audit approach that can:
- Assess security controls across hybrid environments
- Monitor distributed access points and data flows
- Validate security measures for remote and on-premise operations
- Ensure consistent policy enforcement across the technology stack
Why traditional data security audits won’t cut it
Traditional audit approaches that worked a decade ago are breaking under the weight of modern enterprise requirements. Let’s examine why legacy processes are failing to meet today’s demands.
1. The manual evidence burden
Compliance teams spend countless hours chasing screenshots, updating spreadsheets, and managing version control across hundreds of evidence items. This manual approach isn’t just inefficient—it’s a major source of errors and delays. When evidence gathering is one of the most time-consuming parts of an audit, strategic security improvements take a back seat to administrative tasks.
2. Organizational silos
The disconnect between compliance, IT, and security teams creates a fragmented audit process. Evidence requests bounce between departments, context gets lost in email threads, and duplicated efforts waste valuable resources. Without a centralized system, teams struggle to maintain audit momentum and transparency.
3. Modern infrastructure complexity
Today’s enterprise architectures span multiple clouds, on-premises systems, and edge devices. Traditional audit processes weren’t designed for this distributed reality. Tracking security controls across hybrid environments requires a more sophisticated approach than legacy checklist-based methods can provide.
4. Keeping pace with evolving threats
Traditional audit processes struggle to address modern security challenges like fileless malware, zero-day exploits, and AI-powered attacks. When evidence collection takes months, your security assessment is outdated before it’s complete. Today’s threat landscape demands real-time visibility and continuous control validation.
5. Audit fatigue
The endless cycle of evidence collection, review, and updates is burning out enterprise teams, especially when managing multi-framework compliance. When one audit ends, another begins, leaving no time for process improvement or strategic planning. This constant pressure leads to rushed submissions, incomplete documentation, and increased compliance risk.
6. Unpredictable timelines and costs
Traditional audits are plagued by scope creep and hidden costs. What starts as a straightforward certification often expands into months of back-and-forth with auditors, additional evidence requests, and mounting consulting fees. This unpredictability makes it impossible to budget effectively or plan resource allocation.
The modern approach to data security audits
After years of struggling with inefficient audit processes, forward-thinking enterprises are embracing a new paradigm. By leveraging modern technology and strategic approaches, organizations can transform data security audits from a dreaded burden into a streamlined, predictable process that strengthens their security posture.
The power of automation
Manual evidence collection is becoming obsolete. Purpose-built platforms now automate the most time-consuming aspects of security audits, from evidence gathering to control tracking. This shift reduces audit cycles by up to 50% while improving accuracy and completeness. Teams can finally focus on strategic security improvements instead of administrative tasks.
Framework integration: Upload once, comply with many
Leading organizations are abandoning the siloed approach to compliance frameworks. Modern platforms map controls across multiple standards, allowing evidence to simultaneously satisfy requirements for ISO 27001, SOC 2, and other frameworks. This integrated approach eliminates redundant work and accelerates multi-framework certification.
Continuous compliance monitoring
The days of point-in-time assessments are over. Real-time monitoring and automated control validation ensure your organization maintains continuous compliance between formal audits. This proactive approach catches issues early, reduces audit preparation time, and provides ongoing assurance to stakeholders.
Collaborative compliance
Modern platforms create a single source of truth where compliance teams, IT staff, and auditors can collaborate efficiently. Centralized evidence repositories, automated workflows, and real-time status tracking eliminate the communication gaps that traditionally delay audits and frustrate teams.
AI-powered intelligence
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the audit process by:
- Automating evidence collection and validation
- Identifying control gaps and suggesting remediation steps
- Predicting compliance issues before they impact audit outcomes
- Streamlining document review and classification
- Providing intelligent insights for continuous improvement
How Thoropass revolutionizes the data security audit
While modern audit approaches offer significant improvements over traditional methods, enterprise organizations need more than just better tools—they need a complete solution that transforms audits. This is where Thoropass stands apart.
- Purpose-built platform: Thoropass was purpose-built to handle the most demanding enterprise audit requirements. Our platform doesn’t just manage evidence—it orchestrates the entire audit process across your organization:
- Automated control mapping across complex technology stacks
- Intelligent evidence collection that adapts to your infrastructure
- Custom workflows that align with enterprise approval processes
- Scalable architecture that grows with your compliance program
- Multi-framework capability: Beyond basic framework mapping, Thoropass delivers genuine multi-framework optimization:
- Upload evidence once and automatically satisfy requirements across ISO 27001, SOC 2, and other frameworks
- Smart control mapping that identifies overlap opportunities
- Cross-framework reporting to demonstrate compliance status across all standards
- Streamlined certification processes that reduce audit cycles by 67% on average
- Expert-guided success: Technology alone isn’t enough. Thoropass pairs our platform with seasoned compliance professionals who understand enterprise complexity:
- Dedicated compliance advisors who’ve managed enterprise audits
- Strategic guidance on framework selection and scope optimization
- Best practices from hundreds of successful enterprise implementations
- Direct auditor collaboration to prevent evidence gaps and delays
- Predictable costs and timelines: We’ve engineered variability out of the audit process with:
- Clear timelines based on your specific framework requirements
- Transparent pricing with no hidden fees or scope creep
- Automated evidence collection that eliminates manual delays
- Real-time status tracking across all workstreams
- Proven methodology that consistently delivers on-time completion
By combining cutting-edge technology with deep compliance expertise, Thoropass doesn’t just improve the audit process—we transform it.
Ready to learn more? Schedule a demo today!
CASE STUDY
Elpha Secure achieves SOC 2 renewal 90% faster than average
Elpha Secure, a cybersecurity software for insurance companies, breezed through SOC 2 recertification thanks to Thoropass.
Frequently Asked Questions
A data security audit is a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s information security controls, policies, and procedures to ensure the protection of sensitive data and compliance with relevant regulatory requirements. Unlike basic security assessments, a thorough data security audit examines both technical controls and organizational processes that safeguard critical information assets.
For enterprise organizations, data security audits typically encompass multiple layers of evaluation, including infrastructure security, access controls, data handling procedures, and incident response capabilities. These audits serve as both a compliance mechanism and a strategic tool for identifying potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
The scope of a data security audit varies based on industry requirements and regulatory frameworks. For example, healthcare organizations might focus heavily on HIPAA compliance and patient data protection, while financial institutions may prioritize SOX requirements and financial data security. Modern enterprises often need to satisfy multiple frameworks simultaneously, making comprehensive data security audits increasingly complex but essential for maintaining a strong security posture.
Data security audits typically fall into several key categories for enterprise organizations based on scope, purpose, and who conducts them. Each type serves a distinct role in maintaining a comprehensive security and compliance program.
Internal security audits are conducted by an organization’s own compliance or security teams. These audits provide regular checkpoints for security controls and compliance readiness, allowing organizations to ensure employees are following proper security measures and identify and address issues before external audits. While cost-effective, internal audits work best as part of a continuous monitoring strategy rather than a standalone compliance solution.
External security audits are performed by independent third-party auditors and are typically required for formal certifications like SOC 2 or ISO 27001. These assessments provide an objective evaluation of security controls and often carry more weight with stakeholders and customers. For enterprises managing multiple frameworks, working with experienced external auditors who understand framework overlap can significantly streamline the certification process.
Specialized audits focus on specific aspects of data security or regulatory requirements. These may include HIPAA security audits for healthcare organizations, PCI DSS audits for payment card data, or targeted assessments of cloud infrastructure security. Modern enterprises often need to manage multiple specialized audits simultaneously, making an integrated approach to evidence collection and control validation essential.
A comprehensive data security audit examines several critical components that work together to protect enterprise data assets. Understanding these components helps organizations build more effective security programs and streamline their audit processes.
Access controls and identity management form the foundation of data security. This component evaluates how organizations manage user permissions, implement role-based access, enforce strong authentication policies, and maintain access logs. For enterprises with complex organizational structures, this includes reviewing privileged access management systems and ensuring appropriate segregation of duties across teams and departments.
Network security infrastructure assessment examines the organization’s defense mechanisms against external and internal threats. This includes evaluating firewall configurations, network segmentation, intrusion detection systems, and VPN security. Modern enterprises must also assess cloud security controls and ensure consistent security policies across hybrid environments.
Data encryption and protection measures safeguard sensitive information both at rest and in transit. Auditors evaluate encryption protocols, key management practices, and data classification policies. This component has become increasingly critical as enterprises manage sensitive data across distributed systems and cloud platforms.
Security monitoring and incident response capabilities demonstrate an organization’s ability to detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents. This includes reviewing security information and event management (SIEM) systems, incident response procedures, and business continuity plans.
Policy and governance frameworks ensure that technical controls align with organizational objectives and compliance requirements. This component examines security policies, risk assessment methodologies, and how security requirements are communicated throughout the organization.
An enterprise data security audit requires a structured approach that balances thoroughness with efficiency. While specific requirements vary by framework, successful audits typically follow a strategic process that ensures comprehensive coverage while minimizing operational disruption.
- Begin with comprehensive scoping and planning: This critical first phase involves defining audit objectives, identifying relevant frameworks, and mapping key stakeholders. For enterprises managing multiple compliance requirements, this phase should identify opportunities to streamline evidence collection across frameworks. Document your current security policies, system inventories, and data flows to establish a clear baseline for assessment.
- Next, implement a systematic evidence collection process: Modern enterprises are moving away from manual spreadsheet tracking toward automated platforms that can gather and validate evidence across complex technology stacks. Focus on collecting evidence that demonstrates both the design and operational effectiveness of your security controls. This includes system configurations, access logs, security policies, and documentation of security procedures.
- Conduct thorough control testing and validation: This phase evaluates whether security controls operate as intended and meet framework requirements. For enterprises with mature security programs, this often includes automated control monitoring and continuous compliance validation rather than point-in-time assessments.
- Finally, analyze findings and develop an actionable audit report and remediation plan: Prioritize identified gaps based on risk level and compliance impact. Document not just what needs to be fixed, but also root causes and preventive measures to strengthen your security program long-term. Modern audit platforms can help track remediation progress and maintain evidence of improvements for future audit cycles.
An enterprise security audit checklist is a structured framework for evaluating an organization’s security controls and compliance readiness. While traditional checklists focused on basic control verification, modern enterprises require more sophisticated assessment tools that align with complex regulatory requirements and dynamic threat landscapes.
A comprehensive security audit checklist typically covers several critical domains:
Infrastructure security
- Network architecture and segmentation
- Cloud security configurations
- Endpoint protection measures
- Vulnerability management processes
- Security monitoring capabilities
Access management and authentication
- Identity and access management (IAM) controls
- Multi-factor authentication implementation
- Privileged access management
- User provisioning and de-provisioning procedures
- Access review processes
Data protection
- Encryption standards and implementation
- Data classification policies
- Data retention and disposal procedures
- Third-party data handling requirements
- Backup and recovery protocols
However, enterprises should view checklists as starting points rather than comprehensive solutions. Modern compliance programs require continuous monitoring and validation beyond static checklists. Leading organizations are moving toward dynamic assessment frameworks that adapt to changing regulatory requirements and emerging security threats while maintaining evidence of continuous compliance.
Regular data security audits deliver strategic value beyond basic compliance requirements. For organizations managing complex technology environments and multiple regulatory frameworks, consistent audit processes provide critical insights that strengthen overall security posture and operational efficiency.
- Risk management and threat prevention represent the primary benefit. Regular audits help enterprises identify and address security gaps before they can be exploited, significantly reducing the risk of costly data breaches. With the average breach now costing enterprises over $4.88 million (IBM), proactive security validation through regular audits becomes a critical risk management tool. Beyond immediate threats, systematic audits help organizations track emerging risks and adapt security controls accordingly.
- Operational efficiency and cost control emerge as key advantages of regular audit cycles. While ad-hoc approaches often lead to rushed preparations and resource strain, established audit processes allow enterprises to streamline evidence collection, reduce redundant work across frameworks, and maintain continuous compliance. Organizations with mature audit programs typically see significant reductions in audit preparation time and resources, allowing teams to focus on strategic security improvements rather than reactive compliance tasks.
- Stakeholder trust and business growth become natural outcomes of consistent security validation. Regular audits demonstrate a commitment to data protection that resonates with customers, partners, and regulators. For enterprises operating in regulated industries or handling sensitive data, the ability to quickly demonstrate compliance through regular audits can accelerate sales cycles and strengthen business relationships. Moreover, maintaining continuous audit readiness enables organizations to pursue new business opportunities without lengthy compliance preparations.
Several key improvements can dramatically enhance efficiency and effectiveness for enterprises looking to transform their audit programs from resource-draining exercises into strategic assets. Here’s how to elevate your audit process to meet modern enterprise demands.
- Start by conducting a thorough evaluation of your current audit practices. Map out existing workflows, identify bottlenecks, and quantify time spent on manual tasks. Look specifically for redundant evidence collection processes, communication gaps between teams, and areas where audit cycles consistently exceed planned timelines. This baseline assessment will help prioritize improvements for maximum impact.
- Invest in purpose-built audit technology that matches enterprise requirements. Legacy tools like spreadsheets and shared drives can’t scale to meet complex compliance needs. Modern audit platforms should offer automated evidence collection, multi-framework mapping, and real-time collaboration capabilities. Look for solutions that integrate with your existing tech stack and provide clear ROI through reduced audit cycles and resource requirements.
- Centralize your compliance operations around a single source of truth. Scattered evidence repositories and siloed documentation create unnecessary complexity and increase risk. Implement a centralized system that maintains current evidence, tracks control effectiveness, and provides clear audit trails. This approach streamlines audits and strengthens your overall security posture through better visibility and control.
- Break down organizational silos through improved collaboration tools and processes. Effective audits require seamless coordination between compliance teams, IT staff, security personnel, and external auditors. Implement platforms and workflows that facilitate real-time communication, clear task ownership, and transparent status tracking across all stakeholders.
- Finally, build for the future with continuous compliance capabilities. Point-in-time assessments no longer suffice in today’s dynamic regulatory environment. Invest in continuous monitoring tools and automated control validation to maintain constant audit readiness. This proactive approach reduces audit preparation time while providing better security assurance between formal assessments.
Financial Technology (FinTech) drives repeatable, secure processes that promote fast, safe, and user-friendly transactions. It is one of the most complex and highly volatile regulatory landscapes with significant stakes for financial institutions and their customers. Adding to these complexities is the need to ensure compliance over multiple jurisdictions and the costs, in terms of both human resources and IT resources, associated with its maintenance, given that granular controls change continuously.
Compliance solutions that can scale dynamically in an automated environment are essential to a financial organization’s success. We’ll provide a comprehensive overview of the FinTech compliance landscape and show how DuploCloud and Thoropass can automate the lion’s share of work, drastically reducing the manual effort required by your team and putting your most seamless compliance journey within reach.
Why compliance is crucial in FinTech
Failure to pass compliance audits in almost any industry results in hefty fines and catastrophic damage to reputation. In FinTech, the risks are magnified exponentially.
- A high-profile data breach or hack can bring down even the most resilient and time-tested bank or brokerage, driving it to dissolution or bankruptcy. The loss of consumer or industry trust can resonate throughout financial markets, imperiling global stability.
- Failed audits generally result in even closer scrutiny by regulatory boards, increasing the risk of elevated operational costs amidst more frequent and rigorous audits.
- As FinTech companies often operate globally, non-compliance in one jurisdiction can have cascading effects across multiple regions, complicating international operations and regulatory relationships.
Building an audit and compliance roadmap
At the core of a successful compliance framework is a roadmap—a strategic plan for creating a closed-loop, predictable process for meeting and exceeding FinTech compliance standards that scale as your customer base expands. However, with so many frameworks and regulations, it can be hard to know where to begin.
Choosing the proper compliance framework
What should a FinTech company search for when building a foundational roadmap? How much should they invest in financial and human resources? How do you know if it’s a solution that will sync with your future needs?
- Analyzing the data you store and transmit – The type of customer data you store and transmit directly drives which compliance framework you aim to satisfy. Below are the two most common frameworks in FinTech.
- SOC 2 tests an organization’s internal controls over a security program and is the most generally sought-after standard. It provides checks and balances to prove to your customers that you’re securing their data in the manner you represent. For any product to be available in the US market, SOC 2 is a mandatory standard.
- PCI is the most common specific standard, focusing on network security, data protection, and card payment data access control. PCI compliance examines how cardholder data is protected, segmented, and stored. Depending on transaction loads, PCI audits have up to four levels, each bearing greater detail and scrutiny.
Any planning you do when creating a framework is pointless if that solution constantly requires a recurring investment to keep it in line with evolving standards and practices. Your customers may have more nuanced needs depending on the vertical markets in which they transact business, and understanding their security requirements is essential.
Cloud-based compliance implementation and optimization
Once a flexible and adaptive framework is in place, the next challenge is to ensure that it is implemented correctly in the most automated and least stressful way possible. This is where products like DuploCloud play a crucial role, as they help streamline the process and enhance efficiency. One key aspect of this implementation is understanding the CIA triad, which consists of three foundational pillars of network security essential for compliance standards.
The CIA (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability) triad
The security triad is defined by:
- Confidentiality – Ensuring no one sees confidential information except those accessing it, shielding against data hacks and breaches.
- Integrity – Ensuring the data is legitimate. An example might be guarding against data doctoring that can be construed as fraudulent.
- Availability – Guarding against malicious (ransomware) and non-malicious availability events. The recent Crowdstrike attack is an excellent example of a non-malicious event that was the most significant disaster recovery effort in recent years.
Portfolio discovery and analysis
Transitioning the concepts of the CIA triad into practical applications begins with the discovery and analysis phase. This phase comprehensively examines an organization’s systems, data, and security requirements. The goal is to understand the existing setup, identify potential risks, and outline necessary enhancements. Below are the the components you are measuring against:
- Identity Management
- Network Security
- Access Controls
- Logging Strategies
- Data Hardening Vulnerability and Patch Management
- Endpoint protection Monitoring and Alerting
- Disaster Recovery
Aligning security foundations
Following the discovery phase, reviewing any additional contractual security obligations is essential. These requirements often complement unique regulatory and statutory obligations. For instance, while you offer PCI Level 3 protection by default, a client may need PCI Level 1. To build a robust security strategy, the following frameworks are employed:
- AWS Cloud Adoption Framework – Designed to help users migrate to the cloud, emphasizing business alignment, risk mitigation, operational efficiency, and other strategic benefits.
- AWS Well-Architected Framework – Assisting cloud architects in building secure, high-performing, resilient, and efficient infrastructure for their applications.
- AWS Shared Responsibility Model – Clarifying the responsibilities of AWS as a cloud service provider and the customer’s responsibilities.
DuploCloud provides insights to improve both the performance and efficiency of tasks in the customer’s realm of the shared responsibility model and, in the process, shift some of the workload to AWS based on those adjustments. The end goal should be to place the burden of responsibility where it makes the most sense from a business perspective.
Managing and implementing compliance controls
Compliance measures are included right from the beginning with DuploCloud. Although compliance controls differ vastly between standards, they are all exceedingly complex and depend on your size, workload, and many other variables. Addressing these requirements early on makes it easier to implement them later—you only use components that meet the necessary compliance criteria.
Comprehensive architectural and network documentation
DuploCloud provides a detailed diagram depicting the agreed-upon architecture and network configurations that align with your security and compliance needs. This ensures that all security and compliance requirements are clearly outlined. These mesh with controls that vendors such as Thoropass help you identify when building your Audit and Compliance Framework. Combining the expertise of Thoropass and DuploCloud ensures synchronicity between your audit-approved framework and the implementation of that framework.
In addition, DuploCloud outlines and tunes your DevOps Automation Lifecycle Model, ensuring seamless integration of CI/CD, Application Provisioning, and Application Monitoring in the most efficient way possible.
Implementation phase
The implementation phase is crucial for turning planned strategies into operational realities. This phase is about setting up and configuring the necessary infrastructure and processes to ensure smooth and secure operations. It’s important because it lays the foundation for a reliable and compliant system, ensuring all elements work seamlessly and efficiently. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
- Defining the Landing Zone – Starting with a baseline built on AWS Best Practices, we establish MFA for users, delete default VPCs, close default security groups, ensure encryption of volumes in EC2, and so on. These actions provide a robust security foundation and prepare the environment for further customization.
- Defining the network architecture – We design and implement the network infrastructure. We create VPCs tailored to shared services while keeping them separate to meet compliance requirements. This segregation ensures that sensitive data is protected and the system’s design aligns with regulatory standards.
- Deploy, test, and tune – This step involves deploying the system components, followed by thorough testing to ensure everything functions correctly. We set up monitoring and logging systems to keep track of the system’s performance and potential issues. Disaster recovery policies are also implemented and rigorously tested to ensure the system can recover quickly in case of failure. We leave nothing to chance and validate all disaster recovery procedures to ensure readiness.
- Final production cut-over – The last step involves transitioning the system into a live production environment. We carefully schedule and execute the cut-over, ensuring minimal disruption. Our team monitors the process closely to address any issues that may arise, providing a smooth and successful transition to the entire operation.
Continuous improvement
DuploCloud and Thoropass work in tandem to ensure that your framework functions and evolves, ensuring you stay caught up. ISO-27001 Requirement 10.2 serves as a blueprint for continuous improvement. Included here are preparations for future audits, reviews of policies and controls, and reviews of security incidents. We want your security implementation to be dynamic, flexible, and resilient. If you’re out of compliance, you are immediately notified to remediate.
In addition, Thoropass specializes in integrating directly with your cloud platform, ingesting data that provides a detailed picture behind out-of-compliance incidents and guards against them in the future. In the past, this process was highly manual and fraught with potential error. Using Thoropass protects you against any threat that’s previously occurred going forward.
About DuploCloud
Using DuploCloud’s DevOps Automation Platform, you can automate almost all of the best practices listed above. The platform automates quick setup and “set it and forget it” management of flexible and scalable infrastructures and managed services across multiple clouds through automation and a team of seasoned DevOps professionals that provide customization according to your security and compliance needs.
In a world of 5-star Yelp reviews and confirmed purchaser Amazon reviews, most of us think we can trust our judgment when it comes to choosing the right auditor. But pay for play reviews are one thing when you are purchasing dinner or shoes. Getting reliable reviews–and having reliable trust–in your auditor for your infosec compliance audit is something altogether different.
It is more important than ever to be sure that the firm you rely on to assess your compliance across a multitude of compliance frameworks and regulations – SOC reporting, HITRUST, HIPAA, PCI, and ISO 27001 to name a few – is a true and valid partner for your business. Not getting it right can have material consequences. To help you conduct your due diligence on your SOC reporting auditor, we put together this 6-step guide to help you make an informed decision.
You can also watch Thoropass’s CEO & Co-Founder Sam Li, and Managing Audit Partner, Leith Khanafseh discuss this important topic in this short video:
Why it’s more important than ever
Having been an auditor and compliance expert for my entire career, I’ve collected an unfortunate number of horror stories from companies who were stuck in challenging situations. Their individual stories are unique, but they almost always come back to one of these issues:
- The audits the firm produces are not in line with the professional standards
- The firm itself is not a licensed CPA firm
- The audit firm is not licensed to conduct audits in the state where the customer is based
- The audit firm “partners” with a compliance automation vendor, but forces the customer to use another platform for the audit
- The compliance software vendor offers a long list of potential auditors without having done any due diligence themselves on the qualifications of that audit firm
As more and more firms rush into the infosec audit space, these horror stories are unfortunately becoming more common. In one recent example, a SOC 2 Type 2 report we reviewed showed that the audit firm only tested controls at a point in-time when the requirements for Type 2 require an evaluation of controls over a period of time. This material deficiency renders the SOC 2 Type 2 report invalid, and puts the company at risk for sharing an invalid SOC 2 Type 2 report.
When any of these things happen, the ramifications can be significant. An invalid audit report, lack of trust with procurement and legal teams, and loss of reputation can all lead to significant business losses. The victim in these situations is the business trying to do the right thing. This is why proactively vetting an auditor is increasingly salient.
Auditing the auditors
If the key to real estate is “location, location, location,” the key to auditors is “reputation, reputation, reputation.”
Every company seeking an infosec audit–whether for the first time or for renewal with a new firm–needs to perform their due diligence on not just the compliance automation software (e.g. how compliance automation software can help automate evidence collection, preparation, and scoping) but also the auditor and the audit reports that they will produce.
Knowing what to expect from an auditor is not unlike knowing a lender, financial planner, or even doctor. It all comes down to trust, and trust is best proven by long reams of evidence and/or experience. Barring that, businesses looking for a new auditor should consider these steps in performing diligence:
Step 1: Verify licenses and qualifications:
Always start by verifying the auditor’s licenses and qualifications. The licenses should be both on the firm level and the individual auditor. For example, for SOC 2 audits, they must be performed by a licensed CPA firm, signed off on by an individual that is a CPA, and the firm must be enrolled in the AICPA Peer Review Program. You can verify each of these requirements through the links below:
CPA firm licenses and individual CPA licenses: Use CPA Verify to verify both the firm and the reporting partner’s licenses (these are two different licenses). Remember, the CPA firm must be registered in the state they do business in and the state of your corporate headquarters. Reciprocity may apply depending on the state. If in doubt, reach out to the state board of accountancy where your corporate HQ is located and verify directly with them. Most of them will have their own databases where you can search.
Step 2: Review experience and expertise
Evaluate the auditor’s experience in conducting information security audits either in your specific industry or in multiple industries (if you desire a diverse background for context.) Experience in auditing similar-sized companies can often be a good indicator of their ability to work with you and meet your needs.
Step 3: Do you due diligence and request references
Request references from past customers who have undergone audits conducted by the auditor. Any auditor with relevant experience should be able to provide case studies, samples, and/or contact information for past customers who can speak to their professional and successful engagement.
Review sample audit reports and documentation provided by the auditor. This will give you insights into their reporting style, clarity, and the depth of their analysis. Ensure that their reports are comprehensive, address all relevant areas, and meet the structural requirements of that framework.
Step 4: Understand audit methodology
Inquire about the auditor’s audit methodology and approach. Ensure that their methods align with industry best practices and professional standards. This is especially important if you’re using a compliance automation software. No matter what the compliance automation software tells you about their technology, the auditor is required by each and every information security standard to perform procedures on the evidence they rely on during the audit. That is, the auditor must verify any automation or automated evidence used in an audit through inspection of each integration and each source system. An auditor in compliance with the professional standards will never blindly trust a third party software without the appropriate verification.
Step 5: Set Communication Expectations
Assess the auditor’s communication skills and their ability to collaborate with your internal teams. Determine how closely you want to work with your auditor and how responsive they are likely to be when you need them, both during and after the audit. Clear, consistent communication is key to a successful audit process.
Step 6: Consider legal and ethical implications
Check if the auditor carries professional liability insurance. This can provide an additional layer of protection in case of errors or omissions during the audit process.
Sometimes diligence can start with a simple Google search: do the details on their website match their documents? Are there good reviews for their services? Look for consistency and transparency. Ensure that the auditor follows legal and ethical guidelines. This includes respecting confidentiality, disclosing any potential conflicts of interest, and conducting the audit in a transparent and unbiased manner.
To verify whether or not the CPA firm is registered in the AICPA Peer Review Program, you can check the AICPA Peer Review Program Public File Search. Once you verify, ask the auditor for their most recent peer review to verify the results.
In addition to the CPA license requirement to issue SOC reports, infosec auditors should also have information security certifications. Common certifications for infosec auditors include Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), and various cloud service provider certifications. Confirm that the auditor holds relevant and up-to-date certifications.
You get what you pay for
Remember, if it seems to good to be true, it probably is.
Pursuing compliance reports is not always a company’s top priority. As a result, the discovery process can be last minute and performed with incomplete priorities. While it makes sense to consider things like price and ubiquity as part of this exploration, those should never be the deciding factors. Compliance is simply too important for your business.
At Thoropass, we’re transparent about our process, experience, and results. Our customer team onboards customers and never leaves their sides. And our auditors meet customers upfront, seamlessly receive evidence from the platform when it’s time for audit, and produce reports that are universally accepted and best in class.
You can read more about our dedication to transparency and excellence here.
Regardless of which compliance or audit solution you go with, I encourage you to do the diligence on the most important part of the process–the auditor and the audit report–before they make any decision.
Eva Pittas is the president and COO of Thoropass. She has over 20 years of experience in the financial industry.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is the compliance framework underpinning a multitude of the digital payments that you and your company likely use every day. This critical data security standard is a minimum requirement to avoid data breaches and protect cardholder data at all times. Pretty important, I’d say, and yet, beyond the security and compliance experts running point in an organization, most business leaders do not have full appreciation and visibility into this security standard.
Non compliance with PCI DSS could bring significant financial and reputational risks.
Consider these numbers:
- 43.4% of companies were fully PCI DSS compliant (v 3.2.1) in 2020
- Despite being less than half of those surveyed, this number was up from a recent low of 27.9% fully compliant just a year prior
- All the while, contactless mobile payments are expected to hit $1-billion dollars this year, and digital wallet usage will go past $10-trillion by the end of 2025
The news that PCI compliance is going up is, of course, encouraging, especially in light of the eye-popping numbers related to digital payments just around the corner. However, the fact that less than half of reporting businesses are already PCI compliant is troubling. We should be even more aware of potential concerns when reading that of those companies who aren’t fully compliant, only 30.1% use some compensating controls from PCI. In these cases, businesses think doing some of the work is enough.
This perspective is wrong: a business is only covered by PCI DSS when it’s fully compliant with not past PCI DSS versions, but the latest. In conjunction, that framework is at the heart of a business’s annual and evolving strategy.
The essentials of PCI
Most CISOs–and especially those in FinTechs–already know about PCI DSS compliance and its centrality in processing, storing, and transmitting data related to digital payments. But with this ubiquity comes blindspots.
Understanding the risks at stake is increasingly important, and is one reason why CISOs must champion PCI DSS compliance as they advocate for its adoption and centrality to every level of their business.
Like almost any compliance framework properly adopted, PCI DSS compliance is not merely a checkbox exercise; it is a strategic approach to fortify defenses against potential breaches. CISOs must recognize that adhering to PCI DSS is not just about following a set of guidelines; it’s a legal and regulatory imperative. Failure to comply can lead to fines, legal actions, and even the revocation of the ability to process credit card transactions.
Getting ahead of the March 31st deadline
Simply put: now is the time to act.
On March 31, 2024, the previous version of PCI DSS (v 3.2.1) will officially be retired. After that date, PCI DSS v 4.0 represents the most updated version of the important security framework. Companies have one year (up to March 31, 2025) to fully implement PCI DSS v 4.0.
Thoropass has covered the changes to this new version, including highlighting the 64 new requirements that are included. These new requirements are designed to keep pace with the growing demand for digital payments, and the growing risk of breaches and attacks.
Consider again how even PCI-aware companies are often not fully compliant. For example, Requirement 11 of PCI DSS which asks companies “to regularly test security systems and processes” was the least enforced aspect of PCI compliance in 2020, at just 60% of companies.
The new version in April 2024 gives every company the opportunity to reexamine their digital payment compliance and ask if they’re compliant enough in this changing economic environment.
Reasons to act now
There are infinite number of reasons to act now when (re)examining your company’s PCI compliance. Among them, consider:
- Fines for not being compliant range from $5,000-100,000 (or more) per month
- 7 out of 10 consumers would be less likely to do business with an organization who had been breached
- The average data breach costs in 2023 were $9.5-million dollars
Whether you’re motivated by money, trust, or fear, the only way to ensure that your company is prepared to meet the future of our economic reality is to protect your company from unforced errors. The easiest and most accepted way to do so is to get fully compliant in PCI DSS.
Are you compliant?
Are you compliant enough?
Are you sure?
No matter how you answer these questions the most important thing is that you have a response that you’re sure of and that remains the same in March, April, and months to follow.


